This document explains how to connect Tomcat to the popular open source web server, Apache. It was originally part of Tomcat: A Minimalistic User's Guide by Gal Shachor, but has been split off for organizational reasons. It should be considered a work in progress. Since the Tomcat source tree is constantly changing, the information herein may be out of date. The only definitive reference at this point is the source code.
This does explain why many Java based web applications (you can host these here on our Tomcat hosting plans) are normally deployed to environments that support a wide array of technologies that are found in a web container/server such as JavaServer Pages (JSP), JDBC and servlets. In such a scenario, a Tomcat application server comes in very. Apache Tomcat provides the basic feature of web server processing for the relevant servlets. It supports the java servlet lifecycle that are init,service and destroy phases. It is the preferred web server software for Java implementations The latest stable release of a tomcat version 9.0.21 was released on June 7 th, 2019.
Other important documents:
- mod_jk HOWTO [??? should be rolled into tomcat-apache howto]
Other Tomcat-Apache HOWTOs: [should be integrated into this one?]
- Howto Configure Tomcat 3.1 with Apache by Freddie Mendoza
- Apache Web Server / JServ / Tomcat / SSL Installation on UNIX by Jan K. Labanowski
- Tomcat and JServ by Jun Inamori
- http://www.dmz.hitachi-sk.co.jp/Java/Tech/servlet/tomcat.html in Japanese
Table of Contents
- [write me]
Apache - Tomcat Cooperation - Sample Server Integration
Up until now we have not discussed Tomcat as a server add on, instead we have considered it as a stand-alone container and discussed how it can be used. There are however a few problems with this picture:
- Tomcat is not as fast as Apache when it comes to static pages.
- Tomcat is not as configurable as Apache.
- Tomcat is not as robust as Apache.
- There are many sites with long time investment in certain web servers, for example, sites that are using CGI scripts/Server API modules/perl/php. We cannot assume that all of them will want to ditch this legacy.
For all these reasons it is recommended that real world sites use an industrial strength web server, such as Apache, for serving the static content of the site, and use Tomcat as a Servlet/JSP add-on.
Our agenda:
- Cover the fundamental behavior of the web server.
- Explain what configuration is needed.
- Demonstrate this on Apache.
Common Installation and Configuration Problems
This section isn't meant to be your one-stop shop for all troubles Tomcat, but a resource for stumbling blocks common to many first-time Tomcat'ers. See the help section for additional links.
http://webserver:8007/ gives a 500
Beatcleaver torrent. This is what you should see in your tomcat.log file:
HANDLER THREAD PROBLEM: java.io.IOException: Stream broken
By default, Tomcat listens for AJP connections on port 8007. AJP is the protocol used to communicate between the web server and Tomcat, not Tomcat and your browser. To test your Tomcat installation, FIX ME ?
<Directory> and <Location> directives ignored
Avid pro tools 10 torrent. FIX ME Apache never applies because forwarded to Tomcat.
Web server won't start when Tomcat is running
FIX ME Port conflict.
'Bad command or filename' when executing Tomcat scripts
[FIX ME] UNIX file format on DOS. Because Tomcat is developed on *nix (rather, the jars are built and distributed there), you may have to convert the files to PC (versus UNIX) format.
Starting Tomcat From Another Directory
Setting Tomcat to Cooperate with the Apache Web Server
Web Server Operation
In a nutshell a web server is waiting for client HTTP requests. When these requests arrive the server does whatever is needed to serve the requests by providing the necessary content. Adding a servlet container may somewhat change this behavior. Now the web server needs also to perform the following:
- Load the servlet container adapter library and initialize it (prior to serving requests).
- When a request arrives, it needs to check and see if a certain request belongs to a servlet, if so it needs to let the adapter take the request and handle it.
Things are even more complex when the user wants to set a configuration that uses virtual hosts, or when they want multiple developers to work on the same web server but on different servlet container JVMs. We will cover these two cases in the advanced sections.
What is the Needed Configuration
The most obvious configuration that one can think of is the identity of the servlet URLs that are under the responsibility of the servlet container. This is clear; someone must know what requests to transmit to the servlet container.. Yet there are additional configuration items that we should provide to the web-server/servlet-container combination:
- We also need to provide configuration regarding the available Tomcat processes and on which TCP/IP host/port they are listening.
- We need to tell the web server the location of the adapter library (so it will be able to load it on startup).
- We need to set adapter internal information such as where and how much to log, etc.
Making it on Apache
This section shows you how to configure Apache to work with Tomcat; it tries to provide explanations as well as insight for the configuration directives that you should use. You can find additional information in the jserv install page .
When Tomcat starts up it will automatically generate a configuration file for Apache in TOMCAT_HOME/conf/jserv/tomcat-apache.conf. Most of the time you don't need to do anything but include this file (appending 'Include TOMCAT_HOME/conf/jserv/tomcat-apache.conf') in your httpd.conf. If you have special needs, for example an AJP port other the 8007, you can use this file as a base for your customized configuration and save the results in another file. If you manage the Apache configuration yourself you'll need to update it whenever you add a new context.
Tomcat: you must restart tomcat and apache after adding a new context; Apache doesn't support configuration changes without a restart. Also the file TOMCAT_HOME/conf/jserv/tomcat-apache.conf is generated when tomcat starts, so you'll need to start Tomcat before Apache. Tomcat will overwrite TOMCAT_HOME/conf/tomcat-apache.conf each startup so customized configuration should be kept elsewhere.
The Apache-Tomcat configuration uses Apache core configuration directives as well as Jserv unique directives so it may confuse you at first, there are however two things simplifying it:
- In general you can distinguish between the two directive 'families' by noting that all the Jserv unique directives start with an 'ApJServ' prefix.
- The entire Tomcat related configuration is concentrated in a single configuration file named tomcat.conf, or the automatically generated tomcat-apache.conf, so you can look at a single file.
As you can see the configuration process was split into 4 steps that will now be explained:
- In this step we instruct Apache to load the jserv shared-object (or the NT world dll). This is a well known Apache directive. If the loading went well and the module came from a file named mod_jserv.c (1a) we can start with the rest of the Jserv-Tomcat configuration.
- This step sets various Jserv internal parameters, these parameters:
- Instruct jserv not to start the Tomcat process. Automatically starting Tomcat is not implemented yet.
- Disable the secret key challenge/response between Apache and Tomcat. Again, the secret key work is not implemented yet.
- Instruct jserv to copy the base server mount points (see next section) in case of virtual hosting.
- Instruct jserv to use the notice log level. Other log levels include emerg, alert, crit, error, warn, info and debug.
- This step sets the default communication parameters. Basically it says that the default protocol used for the communication is ajpv12 (do not mess with this one) and that the Tomcat process runs on the same machine and listens on port 8007. If you run Tomcat on a machine other than the one used for Apache you should either update your ApJServDefaultHost or use a full URL when mounting contexts (see next). Also, if you configured the Tomcat connectors to use a port other then 8007, you should update your ApJServDefaultPort or use a full URL when mounting contexts.
- This step mounts a context to Tomcat. Basically it says that all the web server paths that start with /examples go to Tomcat. This ApJServMount example is a rather simple one, in fact ApJServMount can also provide information regarding the communication protocol to be used and the location where the Tomcat process listens, for example: ApJServMount /examples ajpv12://hostname:port/rootmounts the context /examples to a Tomcat process that runs on host 'hostname' and listens on port number 'port'.
Obtaining the Jserv Module (mod_jserv)
As previously stated, we need a web server adapter to sit in Apache and redirect requests to Tomcat. For Apache, this adapter is a slightly modified version of mod_jserv.
You may try to look here and see if there is an already pre-built version of mod_jserv that suites your OS (Usually there is one for NT), however, being a native library you should not expect that yet (too many OS's, not enough developers, life too short..). Moreover, small variations in the way you built Apache/Your specific UNIX variant may result in dynamic linking errors. You should really try to build mod_jserv for your system (don't panic, it is not that hard!).
Building mod_jserv on UNIX involves the following:
- Download the source distribution of Tomcat from here.
- Uncompress it into some directory.
- Building the module:
- Change directory into jakarta-tomcat/src/native/apache/jserv/
- Execute the build command apxs -c -o mod_jserv.so *.capxs is part of the Apache distribution and should be located in your APACHE_HOME/bin.
- Download the source distribution of Tomcat from here.
- Unzip it into some directory.
- Building the module:
- Change directory into jakarta-tomcatsrcnativeapachejserv
- Add Visual C++ into your environment by executing the script VCVARS32.BAT.
- Execute the build command nmake is the Visual C++ make program.
Making Apache Serve your Context's Static Files
The previous Apache-Tomcat configuration file was somewhat inefficient, it instructed Apache to send any request for a resource that starts with the /examples prefix to be served by Tomcat. Do we really want that? There are many static files that may be a part of our servlet context (for example images and static HTML), why should Tomcat serve these files?
You may actually have reasons for doing that, for example:
- You may want to configure Tomcat based security for these resources.
- You may want to follow users requests for static resources using interceptors.
Apache Tomcat Web Server 9.0 Free Download
In general however, this is not that case; and making Tomcat save static files is just a CPU waste. We should instead have Apache serve these static files and not Tomcat. Lets look now at a sample tomcat.conf file that does exactly that:
Having Apache serve the static files requires the following:
- Instructing Apache to send all servlet requests to Tomcat.
- Instructing Apache to send all JSP requests to Tomcat.

As you can see, the beginning of this configuration file is the same as seen in the previous example. The last step (mounting a context), however, was replaced in a long series of Apache and ApJServ configuration directives that will now be explained:
- This step informs Apache of the context location and aliases it to an Apache virtual directory. This way Apache can serve files from this directory.
- This optional step instructs Apache more about how to serve the context; for example you can decide if Apache will allow directory indexing (listing) or set a special index file.
- This step instructs Apache to protect the WEB-INF directory from client access. For security reasons it is important to prevent visitors from viewing the content of the WEB-INF directory, for example web.xml can provide valuable information for intruders. This step blocks the WEB-INF content from visitors.
- This step instructs Apache to serve all the jsp locations within the context using the jserv servlet handler. The servlet handler redirects these requests based on the default host and port.
- This step mounts specific servlet URLs to Tomcat. You should note that you should have as many such mount directives as the number of specific servlet URLs.
- This last step is an example for the addition of servlet only context to Tomcat.
Configuring for Multiple Tomcat JVMs
Sometimes it is useful to have different contexts handled by different JVMs, for example:
- When each context serves a different, specific task and runs on a different machine.
- When we want to have multiple developers work on a private Tomcat process but use the same web server.
 Implementing such schemes where different contexts are served by different JVMs is very easy and the following configuration file demonstrates this:
Implementing such schemes where different contexts are served by different JVMs is very easy and the following configuration file demonstrates this: As you can see in the previous example, using several JVMs (even even those that run on different machines) can be accomplished easily by using a full ajp URL mount. In this full URL we actually specify the host where the Tomcat process is located and it's port.
Had the two Tomcat processes run on the same machine, we would have to configure each of them with different connector ports. For example, assuming that the two JVMs runs on localhost, the Apache-Tomcat configuration should have something that looks like:
Looking at the above file you can see that we have two explicit ApJServ mount points each pointing to a different port on the same machine. It is clear that this configuration requires support from the configuration found in the server.xml files. We will need in these files different <Connector> configurations, for the different Tomcat processes. We will actually need two different server.xml files (lets call them server_joe.xml and server_bill.xml) with different <Connector> entries as shown in the next two samples:
When looking at server_joe.xml you can see that the <Connector> is configured for port 8007. In server_bill.xml (see next) on the other hand the <Connector> is configured for port 8009.
The port configuration is not the only place where the joe and bill configuration differs. We have @@@ marks in the xml files marking the four places where changes had to be made. As you can see, this difference is necessary to avoid the two Tomcat processes from overwriting each other's logs and workspace.
Then we should start the two tomcat processes using the -f command line option:
Configuring Virtual Hosting
It is possible to support virtual hosts under Tomcat Ver3.1, in fact the virtual host configuration is very similar to configuring for multiple JVM (as explained in the previous section) and the reason is simple; in Tomcat 3.1 each virtual host is implemented by a different Tomcat process.
With the current (Ver3.1) Tomcat, virtual hosting awareness is provided by the web server (Apache/Netscape…). The web server virtual hosting support is used by the Tomcat adapter to redirect requests belonging to a certain virtual host to the JVM(s) containing the contexts of this virtual host. This means that if (for example) we have two virtual hosts (vhost1 and vhost2), we will have two JVMs: one running the contexts of vhost1 and the other running the contexts of vhost2. These JVMs are not aware of each others existence, in fact, they are not aware of the concept of virtual hosting. All the virtual hosting logic is inside the web-server adapter. To make things clearer, lets look at the following sample Apache-Tomcat configuration file:
As can be seen, steps 1,2 and 3 define two Apache virtual hosts and for each of them, mount the /examples context to a certain ajpv12 URL. Each such ajpv12 URL points to a JVM that contains the virtual host. The configuration of the two JVMs is very similar to the one demonstrated in the previous section, we will need again to use two different server.xml files (one for each virtual host process) and we will need to start the Tomcat processes with the -f command line option. After doing that we will be able to approach Apache, each time with a different host name, and the adapter will redirect us to the appropriate JVM.
The need for improved virtual host support
Having each virtual host implemented by a different JVM is a huge scalability problem. The next versions of Tomcat will make it possible to support several virtual hosts within the same Tomcat JVM.
Credits
This document was created by Gal Shachor. It was split off into a separate document and revised by Alex Chaffee and Rob Slifka. With help from (in alphabetical order):
- Jonathan Bnayahu
Alex Chaffee
Fiona Czuczman
Costin Manolache
Rob Slifka
Copyright ©1999-2001 The Apache Software Foundation |
Apache Tomcat Tutorial
Welcome to Apache Tomcat Tutorial. Learn to use Apache Tomcat as a JSP container, HTTP Web Server, etc., and understand configuration for security and scalability with examples.
Latest version available is Apache Tomcat 8.5.X.
Apache Tomcat Tutorial – Index
- Managing Tomcat
- Deploying Web Applications with Apache Tomcat
Introduction to Apache Tomcat
The Apache Tomcat software is an open source implementation of the Java Servlet, JavaServer Pages, Java Expression Language and Java WebSocket technologies.
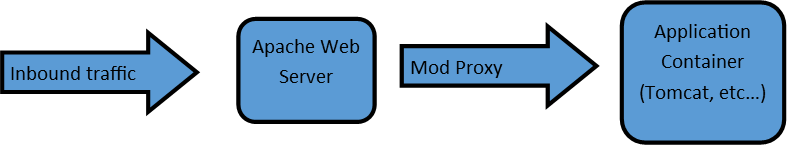
Apache Tomcat is usually used as a Servlet Container even though Tomcat has a fully functional HTTP Server to serve static content. In most of production, Tomcat is used in conjunction with Apache HTTP Server where Apache HTTP Server attends static content like html, images etc., and forwards the requests for dynamic content to Tomcat. This is because Apache HTTP Server supports more advanced options than that of Tomcat.
Latest Apache Tomcat version 8.5 adds support for HTTP/2, OpenSSL for JSSE, TLS virtual hosting and JASPIC 1.1
Components and Features of Apache Tomcat
Apache Tomcat has following components and features to manage web applications.
- Catalina
- Coyote
- Jasper
- Cluster
- High Availability
- Web Application
Jasper 2

Jasper is the JSP Engine for Tomcat. Jasper is responsible for parsing JSP files and compilation of JSP’s Java code as servlets.
Jasper is capable of background compilation, which means if any changes are made to JSP files, then the older versions of those JSP files are still retained by the server, until the updated JSP files are recompiled.
Catalina
Catalina is Tomcat’s servlet container. Catalina makes Tomcat a Web Server for dynamic content.
Coyote
Coyote is the component that makes Tomcat capable as a HTTP Web Server. Coyote makes Catalina also act as a server that serves static content.
Installing Apache Tomcat on Ubuntu
To install Tomcat on Ubuntu, you could use command line interface and run the following command :
If you would like to install tomcat7 for some project related reasons, use tomcat7 instead of tomcat8 in the command.
Following are the useful locations that we may need in furthur steps :
- /etc/tomcat{X} for configuration
- /usr/share/tomcat{X} for runtime, called CATALINA_HOME
- /usr/share/tomcat{X}-root for webapps
You could check if the Tomcat server is running, by opening a browser and hitting the url http://localhost:8080/. Something similar to the following would be responded back with.
Start Apache Tomcat
Apache Tomcat Web Server Tutorial
Once you install Tomcat, it is started automatically.
In case if you have stopped it manually, and would like to start Apache Tomcat again, open a terminal and run the following command.
Restart Apache Tomcat
Apache Tomcat Web Server 9.0
There could be scenarios, like you have updated your web-application, where you may need to restart Apache Tomcat for the server to pickup the changes.
To restart Apache Tomcat, Open a Terminal and run the following command.
Stop Apache Tomcat
To stop Apache Tomcat, Open a Terminal run the following command.
If you have installed tomat7, use tomcat7 instead of tomcat8 in the above command.
Deploying Static Web-Applications with Apache Tomcat
In the following sections, we shall learn to deploy static and web applications in tomcat.
Deploying Static Web-Applications with Apache Tomcat
To deploy static web application with Tomcat, all you need to do is copy your project folder to tomcat web-apps directory.
For Linux :
Now restart Tomcat for the changes to take effect.
Open a broswer, and hit the url, http://localhost:8080/StaticWebProject.
Deploying Dynamic Web-Applications with Apache Tomcat
. Animax card captor sakura dub torrent. war is the format of the web application that Apache Tomcat Server could deploy. If you are building a web application using an IDE like Eclipse, you could export the application as a WAR file.
Conclusion
Apache Tomcat Web Server Download
With these series of tutorials, we have learnt how to configure and work with Apache Tomcat.

